How Mortgage Rates Are Determined: 7 Powerful Factors Revealed
Ever wonder how mortgage rates are determined? It’s not magic—it’s a mix of global economics, lender policies, and your personal finances. Let’s break down the real forces shaping your home loan costs.
How Mortgage Rates Are Determined: The Big Picture

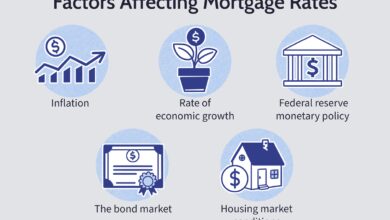
Understanding how mortgage rates are determined starts with recognizing that they are not set by a single entity. Instead, a complex web of economic indicators, financial markets, and institutional policies collectively influence the interest you pay on a home loan. While it may seem like rates appear out of thin air, they are actually the result of carefully monitored economic data and investor behavior.
The Role of the Bond Market
One of the most significant influences on mortgage rates is the bond market—specifically, the yield on the 10-year U.S. Treasury note. Although mortgages aren’t directly tied to Treasuries, they often move in tandem because both are considered long-term investments. When investors flock to safe-haven assets like government bonds, yields drop, and mortgage rates often follow.
- Mortgage-backed securities (MBS) are directly linked to mortgage rates.
- When MBS yields rise, lenders increase mortgage rates to maintain profitability.
- Investor demand for MBS affects how mortgage rates are determined daily.
“Mortgage rates are more influenced by the secondary mortgage market than by the Federal Reserve’s direct actions.” — Investopedia, How Mortgage Rates Work
Inflation and Purchasing Power
Inflation erodes the value of money over time, and lenders must account for this when setting interest rates. If inflation is high, lenders charge higher rates to ensure they receive a real return on the money they lend. This is a core principle in how mortgage rates are determined.
- Higher inflation typically leads to higher mortgage rates.
- The Federal Reserve often raises interest rates to combat inflation, indirectly pushing mortgage rates up.
- Expected future inflation, not just current inflation, impacts long-term mortgage pricing.
How Mortgage Rates Are Determined by the Federal Reserve
While the Federal Reserve doesn’t set mortgage rates directly, its monetary policy decisions have a profound ripple effect across the financial system. The Fed influences short-term interest rates through the federal funds rate, which affects everything from credit cards to adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs).
how mortgage rates are determined – How mortgage rates are determined menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
The Federal Funds Rate and Its Indirect Impact
The federal funds rate is the interest rate at which banks lend to each other overnight. When the Fed raises or lowers this rate, it changes the cost of borrowing across the economy. Although this rate primarily affects short-term debt, it can influence consumer confidence and investment behavior, which in turn affects mortgage rates.
- Rising federal funds rates often signal tighter monetary policy, leading to higher mortgage rates.
- During economic downturns, the Fed may lower rates to stimulate borrowing and spending.
- Markets often anticipate Fed moves, causing mortgage rates to shift before official announcements.
Quantitative Easing and Market Liquidity
During times of economic crisis, such as the 2008 financial meltdown or the 2020 pandemic, the Federal Reserve engages in quantitative easing (QE). This involves buying large quantities of Treasury bonds and mortgage-backed securities to inject liquidity into the market.
- QE increases demand for MBS, lowering mortgage rates.
- When the Fed ends QE or begins “quantitative tightening,” mortgage rates often rise.
- Between 2020 and 2022, QE helped keep 30-year mortgage rates below 3%.
“The Fed’s asset purchases during the pandemic were a major factor in driving mortgage rates to historic lows.” — Federal Reserve History, Quantitative Easing Explained
How Mortgage Rates Are Determined by Economic Indicators
Various economic reports released monthly or quarterly provide signals about the health of the economy. Lenders and investors watch these closely because they influence expectations about future inflation, growth, and monetary policy—all of which affect how mortgage rates are determined.
Employment Data and the Job Market
The Bureau of Labor Statistics’ monthly jobs report, including non-farm payrolls and the unemployment rate, is one of the most closely watched economic indicators. Strong job growth suggests a robust economy, which can lead to higher inflation and, consequently, higher mortgage rates.
- Lower unemployment often correlates with rising mortgage rates.
- Wage growth can signal inflationary pressure, prompting lenders to increase rates.
- Sudden job losses or weak hiring can cause rates to drop as investors seek safer assets.
GDP Growth and Economic Output
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) measures the total value of goods and services produced in the economy. When GDP grows rapidly, it can lead to inflationary pressures, pushing mortgage rates upward. Conversely, slow or negative growth may lead to lower rates.
how mortgage rates are determined – How mortgage rates are determined menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Consistently high GDP growth often leads the Fed to raise interest rates.
- Recessionary periods typically see lower mortgage rates as demand for loans decreases.
- Forecasts of future GDP are often more influential than past data.
Consumer Price Index (CPI) and Inflation Reports
The CPI measures changes in the price of a basket of consumer goods and services. It’s one of the primary tools used to gauge inflation. When CPI rises significantly, lenders anticipate that the Fed will act to cool the economy, which can lead to higher mortgage rates.
- Core CPI (excluding food and energy) is often watched more closely than overall CPI.
- Sustained CPI increases above 2% can trigger rate hikes.
- Unexpected CPI spikes can cause mortgage rates to jump within days.
How Mortgage Rates Are Determined by Lender Policies
While macroeconomic factors set the baseline, individual lenders have the final say in the rates they offer. Each bank or mortgage company evaluates risk, competition, and operational costs when pricing loans. This is where personal factors come into play.
Profit Margins and Operational Costs
Lenders are businesses, and they must cover their costs and make a profit. The interest rate you’re offered includes a margin that accounts for overhead, employee salaries, technology, and risk management.
- Larger banks may offer lower rates due to economies of scale.
- Online lenders often have lower overhead, allowing them to offer competitive rates.
- Local credit unions may offer personalized service but sometimes have higher rates due to limited resources.
Competition Among Lenders
The mortgage market is highly competitive. When one major lender lowers its rates, others often follow to remain attractive to borrowers. This competition can lead to short-term rate drops, especially during peak home-buying seasons.
- Rate shopping can save borrowers thousands over the life of a loan.
- Lenders may offer “rate discounts” or rebates to win business.
- Transparency tools like mortgage comparison websites increase competition.
How Mortgage Rates Are Determined by Borrower-Specific Factors
Even if two people apply for the same type of mortgage on the same day, they may receive different rates. This is because lenders assess individual risk. Your personal financial profile plays a crucial role in how mortgage rates are determined for you.
how mortgage rates are determined – How mortgage rates are determined menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Credit Score and Credit History
Your credit score is one of the most important factors in determining your mortgage rate. Higher scores indicate lower risk, so lenders reward them with lower interest rates.
- Borrowers with FICO scores above 760 typically get the best rates.
- A score below 620 may result in higher rates or loan denial.
- Even a 20-point difference in credit score can affect your rate by 0.25% or more.
“A borrower with a 760+ credit score could save over $200 per month compared to someone with a 640 score on a $300,000 mortgage.” — MyFICO, Mortgage Rates by Credit Score
Down Payment and Loan-to-Value Ratio
The size of your down payment affects your loan-to-value (LTV) ratio. A lower LTV means less risk for the lender, which can lead to a lower interest rate. Putting down 20% or more often eliminates the need for private mortgage insurance (PMI), further reducing costs.
- Higher down payments typically result in lower mortgage rates.
- LTV ratios above 80% may require PMI, increasing overall borrowing costs.
- Some loan programs, like VA loans, offer low rates with no down payment.
Debt-to-Income Ratio (DTI)
Your DTI ratio compares your monthly debt payments to your gross monthly income. Lenders use this to assess your ability to manage monthly payments. A lower DTI is seen as less risky.
- Most lenders prefer a DTI below 43% for conventional loans.
- Borrowers with high DTI may be offered higher rates or required to reduce debt first.
- DTI is especially important for jumbo loans or non-prime borrowers.
How Mortgage Rates Are Determined by Loan Characteristics
The type of mortgage you choose significantly impacts the rate you receive. Different loan products carry different levels of risk and cost for lenders, which is reflected in the interest rate.
Fixed-Rate vs. Adjustable-Rate Mortgages (ARMs)
Fixed-rate mortgages offer stable payments over the life of the loan, while ARMs have rates that can change after an initial fixed period. ARMs often start with lower rates but carry more risk.
how mortgage rates are determined – How mortgage rates are determined menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- 30-year fixed mortgages typically have higher rates than 15-year loans.
- 5/1 ARMs often start 0.5% to 1% lower than 30-year fixed rates.
- ARMs are riskier for borrowers if rates rise after the initial period.
Loan Term Length
Shorter loan terms usually come with lower interest rates because the lender’s money is at risk for a shorter period. However, monthly payments are higher due to the compressed repayment schedule.
- 15-year mortgages often have rates 0.5% to 0.75% lower than 30-year loans.
- Shorter terms result in significantly less interest paid over time.
- Some borrowers refinance from 30-year to 15-year to save on interest.
Loan Type and Government Backing
Different loan programs—such as conventional, FHA, VA, and USDA—have different risk profiles and funding mechanisms, which affect rates.
- VA and USDA loans often have lower rates due to government backing.
- FHA loans may have slightly higher rates but are accessible to borrowers with lower credit.
- Conventional loans with private mortgage insurance (PMI) may have higher effective costs.
How Mortgage Rates Are Determined by Global and Geopolitical Factors
It might seem surprising, but events halfway around the world can influence U.S. mortgage rates. Global markets are interconnected, and investor behavior often shifts in response to international developments.
Global Economic Trends
When economies in Europe, Asia, or elsewhere slow down, investors may move money into U.S. bonds, driving yields down and lowering mortgage rates. Conversely, strong global growth can pull investment away from U.S. assets, pushing rates up.
- European Central Bank policies can affect U.S. bond yields.
- Emerging market crises often lead to a “flight to safety” in U.S. Treasuries.
- Global demand for U.S. debt helps keep long-term rates lower than they might otherwise be.
Geopolitical Events and Market Volatility
Wars, elections, trade disputes, and pandemics can create uncertainty in financial markets. During such times, investors often seek safe-haven assets like U.S. government bonds, which can lower mortgage rates.
how mortgage rates are determined – How mortgage rates are determined menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- The 2022 Russia-Ukraine war caused a temporary dip in mortgage rates due to market fear.
- U.S. political instability can increase market volatility, affecting rate movements.
- Pandemics like COVID-19 led to massive bond buying and record-low mortgage rates.
“In times of global crisis, U.S. Treasury bonds are seen as one of the safest investments, which indirectly benefits mortgage borrowers.” — Council on Foreign Relations, The Role of the U.S. Dollar
How Mortgage Rates Are Determined: Historical Trends and Future Outlook
Looking at historical data helps us understand how mortgage rates are determined over time and what might lie ahead. Rates have fluctuated dramatically over the past century, influenced by wars, recessions, and policy changes.
Historical Mortgage Rate Trends
In the 1980s, mortgage rates soared above 18% due to high inflation. Since then, rates have generally trended downward, reaching historic lows below 3% in 2020–2021. Understanding this context helps borrowers make informed decisions.
- Average 30-year fixed rate was 16.63% in 1981 (Freddie Mac data).
- Rates fell below 3% for the first time in 2020.
- As of 2023, rates have risen above 7% due to inflation and Fed tightening.
Future Projections and Expert Predictions
While no one can predict the future with certainty, economists and housing experts use models to forecast rate trends. Factors like inflation, Fed policy, and housing demand will continue to shape rates.
- Many experts expect rates to stabilize between 6% and 7% in the mid-2020s.
- Long-term trends may depend on government debt levels and demographic shifts.
- Technological advances in lending could reduce costs and improve rate transparency.
How to Prepare for Rate Changes
Borrowers can’t control mortgage rates, but they can prepare for them. Locking in a rate, improving credit, and shopping around are smart strategies.
- Rate locks can protect you from increases during the loan process.
- Improving your credit score before applying can save thousands.
- Comparing at least three lenders ensures you get the best deal.
How are mortgage rates determined by the bond market?
how mortgage rates are determined – How mortgage rates are determined menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Mortgage rates are heavily influenced by the yield on mortgage-backed securities (MBS), which are traded in the bond market. When investor demand for MBS rises, yields fall, and lenders can offer lower rates. Conversely, when MBS yields rise, mortgage rates increase to maintain lender profitability.
Does the Federal Reserve set mortgage rates?
No, the Federal Reserve does not directly set mortgage rates. However, its policies—especially the federal funds rate and quantitative easing—indirectly influence mortgage rates by affecting overall financial conditions, inflation expectations, and investor behavior in the bond market.
Why do mortgage rates change daily?
Mortgage rates change daily because they are tied to financial markets that react to economic data, investor sentiment, and global events. Even minor shifts in inflation reports, employment numbers, or geopolitical tensions can cause rates to fluctuate from one day to the next.
how mortgage rates are determined – How mortgage rates are determined menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Can I negotiate my mortgage rate?
While the base rate is largely determined by market conditions, you can often negotiate lender fees, points, or rate discounts. Shopping around and leveraging competing offers can help you secure a better overall deal, even if the interest rate itself is non-negotiable.
How can I get the lowest mortgage rate possible?
To get the lowest mortgage rate, improve your credit score, make a larger down payment, reduce your debt-to-income ratio, choose a shorter loan term, and compare offers from multiple lenders. Locking in your rate when market conditions are favorable can also save you money.
Understanding how mortgage rates are determined empowers you to make smarter financial decisions. From global bond markets to your personal credit score, multiple factors shape the cost of your home loan. By staying informed and proactive, you can secure a rate that aligns with your goals and saves you thousands over time.
how mortgage rates are determined – How mortgage rates are determined menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Further Reading: