Government Mortgage Loan Rates: 7 Shocking Truths You Must Know
Navigating the world of home financing? Understanding government mortgage loan rates can be your golden ticket to smarter borrowing and massive savings—especially in today’s shifting economic climate.
What Are Government Mortgage Loan Rates?

Government mortgage loan rates refer to the interest rates applied to home loans that are either insured, guaranteed, or directly provided by federal agencies. Unlike conventional loans, these are designed to make homeownership more accessible, particularly for first-time buyers, low-to-moderate income earners, and those in rural or underserved areas. These rates are often more competitive due to government backing, which reduces lender risk.
Federal Agencies Behind Government-Backed Loans
Several U.S. federal agencies play a pivotal role in shaping government mortgage loan rates by insuring or guaranteeing loans. The most prominent include:
Federal Housing Administration (FHA): Offers FHA loans with lower down payments and more lenient credit requirements.These loans are insured by the FHA, allowing lenders to offer lower interest rates.Learn more about FHA loans here.Department of Veterans Affairs (VA): Provides VA loans to eligible veterans, active-duty service members, and surviving spouses.These loans require no down payment and often come with lower government mortgage loan rates due to full federal backing.Explore VA loan benefits.U.S..
Department of Agriculture (USDA): Offers USDA loans for rural homebuyers with low to moderate incomes.These loans feature zero down payment options and competitive rates, supported by USDA guarantees.Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac: While not direct lenders, these government-sponsored enterprises (GSEs) purchase and guarantee many conventional loans, influencing overall mortgage rate trends, including those near government-backed benchmarks.How Government Loan Rates Differ from Conventional RatesOne of the most common misconceptions is that government mortgage loan rates are always lower than conventional rates.While they often are, this isn’t universally true.The difference lies in risk mitigation.Because government-backed loans reduce lender exposure, they typically offer:.
- Lower credit score requirements
- Reduced down payment thresholds (as low as 0% for VA and USDA loans)
- More flexible debt-to-income (DTI) ratios
However, borrowers may pay additional fees—like mortgage insurance premiums (MIP) on FHA loans—that can offset some rate advantages. For example, while a conventional loan might have a slightly higher interest rate, it could be more cost-effective over time if the borrower has strong credit and a 20% down payment, avoiding private mortgage insurance (PMI).
“Government-backed loans are not just for the financially struggling—they’re strategic tools for anyone seeking affordable, sustainable homeownership,” says housing economist Dr. Lena Torres.
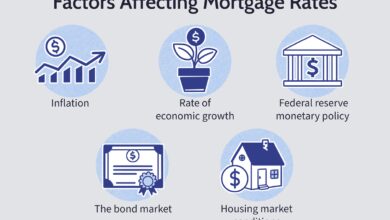
Factors That Influence Government Mortgage Loan Rates
While government backing provides stability, government mortgage loan rates are not set in stone. They fluctuate based on a complex interplay of economic, political, and market forces. Understanding these drivers can help borrowers time their applications for maximum benefit.
1. Federal Reserve Policy and Interest Rates
The Federal Reserve does not directly set mortgage rates, but its monetary policy—especially the federal funds rate—has a strong indirect influence. When the Fed raises rates to combat inflation, borrowing costs across the board increase, including government mortgage loan rates. Conversely, rate cuts can lead to lower rates.
For instance, during the 2020 pandemic, the Fed slashed rates to near-zero, causing a historic drop in 30-year fixed mortgage rates to below 3%. This benefited FHA and VA borrowers immensely. However, in 2022–2023, aggressive rate hikes pushed average government-backed loan rates above 7%, making affordability a major concern.
It’s important to note that mortgage rates are more closely tied to the yield on the 10-year Treasury note than the federal funds rate. When investors demand higher yields on Treasuries due to inflation fears, mortgage rates follow suit.
2. Economic Indicators and Market Trends
Several macroeconomic indicators directly impact government mortgage loan rates:
- Inflation: High inflation erodes the value of future loan repayments, prompting lenders to charge higher rates to compensate.
- Unemployment Rates: Low unemployment signals a strong economy, which can lead to higher rates as demand for credit increases.
- Housing Market Demand: Surges in homebuyer demand—especially during spring and summer—can push rates upward as lenders adjust capacity and risk.
- Consumer Confidence: When consumers feel optimistic, borrowing increases, influencing rate trends.
For example, in early 2023, despite high inflation, government mortgage loan rates for VA loans remained slightly below conventional averages due to strong veteran demand and lender competition in that niche.
3. Borrower-Specific Factors
Even within government-backed programs, individual borrowers receive different rates based on personal financial profiles. Key factors include:
- Credit Score: FHA loans accept scores as low as 500 (with 10% down), but borrowers with scores above 580 qualify for 3.5% down and better rates. A higher score can save hundreds per month.
- Debt-to-Income Ratio (DTI): Lenders prefer DTI below 43%, though some FHA loans allow up to 50% with compensating factors.
- Loan Term: 15-year government-backed loans typically have lower rates than 30-year loans but higher monthly payments.
- Down Payment: Larger down payments reduce lender risk and can lead to better government mortgage loan rates, even on insured loans.
A borrower with a 760 credit score, 20% down, and a DTI of 30% will almost always get a better rate than someone with a 620 score and minimal down payment—even if both use FHA loans.
Types of Government-Backed Loans and Their Rate Structures
Not all government mortgage loan rates are created equal. Each program has unique eligibility rules, cost structures, and rate behaviors. Let’s break down the major options.
FHA Loans: Accessibility with a Cost
FHA loans are among the most popular government-backed options, especially for first-time homebuyers. They offer low down payments (3.5%) and flexible credit standards. However, borrowers must pay both an upfront and annual mortgage insurance premium (MIP), which can make the effective cost of the loan higher—even if the nominal interest rate is competitive.
As of mid-2024, average FHA 30-year fixed rates hover around 6.8%, compared to 6.5% for conventional loans with excellent credit. But for someone with a 600 credit score, the FHA rate might be 0.5% lower than what they’d get on a conventional loan, making it the better choice despite MIP.
Recent changes to FHA MIP—such as extending the duration of annual premiums for loans with less than 10% down—have sparked debate. Critics argue it penalizes lower-wealth borrowers, while supporters say it ensures program sustainability.
VA Loans: The Gold Standard for Eligible Borrowers
VA loans are widely regarded as the most borrower-friendly option. Backed by the Department of Veterans Affairs, they require no down payment, no mortgage insurance, and often come with lower government mortgage loan rates. In 2023, the average VA loan rate was 0.25% to 0.5% below conventional averages.
Eligibility is limited to veterans, active-duty personnel, National Guard and Reserve members with qualifying service, and certain surviving spouses. The VA funding fee—ranging from 1.4% to 3.6%—can be rolled into the loan, but it’s often waived for those with service-connected disabilities.
One major advantage: VA loans allow for rate-and-term refinancing with minimal paperwork through the Interest Rate Reduction Refinancing Loan (IRRRL) program, helping veterans lock in lower government mortgage loan rates quickly.
“The VA loan program is not just a benefit—it’s a well-earned right,” says retired Colonel Mark Delaney, a housing advocate for veterans.
USDA Loans: Rural Homeownership Made Affordable
USDA loans are designed to promote homeownership in rural and suburban areas. They offer 100% financing (no down payment) and competitive interest rates, typically slightly below FHA averages. However, property location is strictly regulated—only homes in designated rural areas qualify.
Like FHA loans, USDA borrowers pay an upfront guarantee fee (1% of the loan) and an annual fee (0.35%), which are factored into the effective cost. But with no credit score minimum (though lenders typically require 640+), and low income limits, these loans are a lifeline for many.
In 2024, USDA 30-year fixed rates average around 6.7%, making them highly competitive. The program also offers streamlined refinancing for existing USDA borrowers, allowing them to reduce payments without a full appraisal or credit check.
How to Find the Best Government Mortgage Loan Rates
Securing the lowest possible government mortgage loan rates requires strategy, timing, and diligence. Here’s how to maximize your chances.
1. Shop Around with Multiple Lenders
Never accept the first rate quote you receive. Lenders vary widely in how they price government-backed loans. Some specialize in VA or FHA financing and offer discounted rates to attract volume. Others may tack on higher origination fees or markup rates.
Best practice: Get quotes from at least three to five lenders, including:
- National banks (e.g., Bank of America, Wells Fargo)
- Credit unions (often offer lower rates to members)
- Online lenders (e.g., Rocket Mortgage, Veterans United)
- Local mortgage brokers (can access wholesale rates)
Use online comparison tools like NerdWallet or Zillow to benchmark current government mortgage loan rates in your area.
2. Improve Your Credit Profile
Your credit score is one of the most powerful levers for lowering your rate. A jump from 660 to 700 can save you 0.5% or more on your government mortgage loan rates. Focus on:
- Paying down credit card balances (aim for under 30% utilization)
- Correcting errors on your credit report
- Avoiding new credit applications before applying for a mortgage
- Setting up automatic payments to avoid late fees
For FHA borrowers, even a 50-point increase can mean the difference between a high-risk and standard-risk pricing tier.
3. Consider Timing and Rate Locks
Mortgage rates change daily—sometimes multiple times a day. Monitoring trends can help you lock in a low rate at the right moment. Financial websites like Freddie Mac’s Primary Mortgage Market Survey provide weekly updates on average government mortgage loan rates.
Once you find a favorable rate, ask your lender about a rate lock—typically valid for 30 to 60 days. Some lenders offer float-down options, allowing you to benefit if rates drop further before closing.
The Impact of Government Policy on Mortgage Rates
Government mortgage loan rates don’t exist in a vacuum. Federal legislation, agency rule changes, and housing policy shifts can dramatically alter the landscape.
Recent Legislative Changes Affecting Rates
In 2023, Congress passed the Supporting Affordability for Homeownership (SAFE) Act, which directed the FHA to evaluate its MIP structure to reduce long-term costs for borrowers. While no immediate cuts were made, the review signaled potential future rate relief.
Additionally, the VA has expanded eligibility to include more National Guard members after recent policy updates, increasing demand for VA loans and encouraging lenders to offer more competitive government mortgage loan rates to capture this market.
The Biden administration’s 2024 housing plan includes proposals to increase funding for USDA loans and expand down payment assistance programs, which could indirectly lower effective rates by reducing borrower risk profiles.
How Inflation and Economic Policy Shape Rates
When inflation surged past 7% in 2022, the Federal Reserve responded with rapid interest rate hikes. This directly impacted government mortgage loan rates, pushing 30-year fixed FHA and VA loans above 7% for the first time since 2007.
However, government-backed loans showed more resilience than conventional ones. Lenders were less likely to pull back on VA and FHA offerings due to the safety net of federal guarantees, ensuring continued access even in tight credit markets.
As inflation cooled to 3.5% in early 2024, mortgage rates began to stabilize. Economists predict that if inflation remains under control, government mortgage loan rates could dip below 6.5% by late 2024—offering a renewed window for affordable homeownership.
The Role of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac
Though not direct government lenders, Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac play a crucial role in shaping the mortgage market. They purchase loans from lenders, package them into securities, and guarantee timely payments to investors. This liquidity allows lenders to offer lower rates.
Both GSEs have introduced loan-level pricing adjustments (LLPAs) that affect government-backed-like loans. For example, a borrower with a 620 credit score and 5% down payment might face a 2.5% LLPA surcharge, effectively increasing their rate. These adjustments are designed to reflect risk but can make government mortgage loan rates appear less attractive for certain profiles.
Refinancing Government-Backed Loans for Better Rates
Refinancing can be a powerful tool to reduce monthly payments, shorten loan terms, or tap into home equity—especially when government mortgage loan rates drop.
VA IRRRL: The Streamlined Refinance
The VA’s Interest Rate Reduction Refinancing Loan (IRRRL) is one of the most efficient refinancing tools available. It requires no appraisal, no credit check, and minimal documentation. The goal is to help veterans secure lower government mortgage loan rates quickly.
As of 2024, veterans can save an average of $200–$300 per month through an IRRRL if rates have dropped by at least 0.5% since their original loan. The funding fee is typically 0.5% and can be rolled into the loan.
One caveat: The IRRRL must result in a “net tangible benefit” to the borrower, such as a lower rate or payment. Cash-out refinancing is not allowed under this program.
FHA Streamline Refinance
The FHA Streamline Refinance program allows existing FHA borrowers to refinance into lower rates with reduced paperwork. Credit checks are often waived, and appraisals are not required.
However, the program has limitations. It’s only available for borrowers who are current on their loans and refinancing into another FHA loan. The new rate must provide a benefit, such as a lower payment or shorter term.
In 2023, the FHA temporarily suspended the streamline program for cash-out refinances due to fraud concerns, but rate-and-term refinances remain active. Borrowers should act quickly when rates drop, as program rules can change with little notice.
USDA Streamlined Assist Refinance
The USDA’s Streamlined Assist program, launched in 2022, allows eligible borrowers to refinance into lower rates without an appraisal or credit score check. It’s designed to help rural homeowners reduce payments and avoid delinquency.
To qualify, borrowers must be current on their loans, the new payment must be lower, and the loan must have been originated before October 1, 2021. The program has helped thousands lock in savings during periods of falling government mortgage loan rates.
Common Misconceptions About Government Mortgage Loan Rates
Despite their popularity, government-backed loans are often misunderstood. Let’s debunk some myths.
Myth 1: Government Loans Always Have the Lowest Rates
While government mortgage loan rates are often competitive, they’re not automatically the lowest. Borrowers with excellent credit (740+) and large down payments may get better deals on conventional loans without mortgage insurance.
For example, a borrower with a 760 score and 20% down might secure a 6.2% conventional rate with no PMI, while an FHA loan at 6.5% would still require MIP, making the total cost higher over time.
Myth 2: Only Low-Income Borrowers Qualify
Eligibility for government-backed loans isn’t solely based on income. VA loans have no income cap. FHA loans are available to anyone who meets credit and down payment requirements, regardless of earnings. USDA loans do have income limits, but they’re set at 115% of the area median, which allows many middle-class families to qualify.
Myth 3: These Loans Are Hard to Get Approved For
While government loans have guidelines, the approval process is often smoother than conventional loans. Automated underwriting systems (like FHA’s TOTAL Scorecard or VA’s ACE) streamline approvals. Many lenders specialize in these programs and can close loans faster than traditional mortgages.
“The biggest barrier isn’t eligibility—it’s misinformation,” says mortgage advisor Sarah Kim. “Too many borrowers assume they don’t qualify when they actually do.”
What are government mortgage loan rates?
Government mortgage loan rates are the interest rates on home loans backed or insured by federal agencies like the FHA, VA, or USDA. These rates are often lower than conventional rates due to reduced lender risk, but they come with specific eligibility requirements and sometimes additional fees like mortgage insurance.
Are VA loan rates lower than FHA rates?
Typically, yes. VA loan rates are often 0.25% to 0.5% lower than FHA rates because they require no mortgage insurance and are fully backed by the federal government. However, actual rates depend on the lender, borrower credit, and market conditions.
Can I refinance my government-backed loan?
Yes. Programs like the VA IRRRL, FHA Streamline, and USDA Streamlined Assist allow borrowers to refinance into lower government mortgage loan rates with minimal paperwork. These options are designed to make refinancing fast and accessible.
Do government mortgage loan rates change daily?
Yes. Like all mortgage rates, government mortgage loan rates fluctuate daily based on economic conditions, Treasury yields, and lender pricing. It’s wise to monitor trends and lock in a rate when favorable.
How can I get the lowest government mortgage loan rate?
To secure the lowest rate, improve your credit score, shop around with multiple lenders, consider timing your application during periods of low rates, and explore refinancing options if rates drop after you close.
Government mortgage loan rates play a crucial role in shaping homeownership accessibility across the United States. From FHA and VA loans to USDA programs, these government-backed options offer competitive rates and flexible terms for millions of Americans. While they aren’t always the cheapest option for every borrower, they provide vital pathways to homeownership for those who might otherwise be excluded. By understanding the factors that influence these rates, shopping wisely, and leveraging refinancing opportunities, borrowers can make informed decisions that save thousands over the life of their loan. In an era of economic uncertainty, knowledge is power—and when it comes to government mortgage loan rates, a little insight can go a long way.
Further Reading: