FHA vs Conventional Loan Interest Rates: 7 Shocking Truths Revealed
Choosing between FHA and conventional loans can feel overwhelming—especially when comparing interest rates. In this deep dive, we break down the real differences, costs, and long-term impacts to help you make a smarter mortgage decision.
FHA vs Conventional Loan Interest Rates: The Core Differences

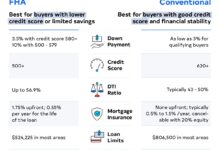
When comparing FHA vs conventional loan interest rates, many borrowers assume one is always cheaper. The truth? It’s more nuanced. While FHA loans are government-backed and often marketed as more accessible, their interest rates aren’t always lower than conventional loans. In fact, recent market trends show that conventional loan rates have sometimes undercut FHA rates, especially for borrowers with strong credit.
How Interest Rates Are Determined
Lenders set interest rates based on risk. FHA loans, insured by the Federal Housing Administration, allow lower down payments (as low as 3.5%) and more lenient credit requirements. Because of this, lenders perceive FHA borrowers as higher risk—potentially leading to higher interest rates. However, this isn’t a hard rule. Conventional loans, backed by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, use automated underwriting systems that can offer competitive rates even to borrowers with mid-tier credit scores.
fha vs conventional loan interest rates – Fha vs conventional loan interest rates menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Credit score plays a major role in both loan types.
- Debt-to-income ratio affects rate eligibility.
- Loan-to-value ratio influences perceived risk.
For example, a borrower with a 640 credit score might get a 7.2% rate on an FHA loan but a 7.0% rate on a conventional loan due to better investor demand for conventional mortgage-backed securities. This counterintuitive outcome highlights why you should never assume FHA = lower rates.
“Interest rates aren’t just about the loan type—they’re about the borrower’s financial profile and current market liquidity,” says mortgage analyst Laura Smith of HousingEcon Insights.
Current Market Trends (2024)
As of mid-2024, average 30-year fixed mortgage rates sit around 6.8% for conventional loans and 7.0% for FHA loans, according to Freddie Mac’s Primary Mortgage Market Survey. While the gap seems small, it can cost thousands over the life of the loan. For a $300,000 mortgage, that 0.2% difference adds up to about $10,800 in extra interest over 30 years.
Market dynamics have shifted. With rising home prices and tighter credit standards, conventional loan investors are more confident in borrower performance, leading to better pricing. Meanwhile, FHA loans, while still popular among first-time buyers, face higher mortgage insurance premiums that indirectly influence rate competitiveness.
fha vs conventional loan interest rates – Fha vs conventional loan interest rates menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Understanding FHA Loan Interest Rates
FHA loans are designed to increase homeownership accessibility, particularly for low- to moderate-income borrowers and those with less-than-perfect credit. But how do their interest rates stack up in real-world scenarios?
Who Qualifies for the Best FHA Rates?
The best FHA interest rates go to borrowers who meet strict criteria despite the program’s flexibility. You’ll need at least a 580 credit score for the 3.5% down payment option, but lenders often impose overlays—additional requirements beyond FHA minimums. For instance, a lender might require a 620 score or higher to offer their most competitive rate.
- Minimum credit score: 580 for 3.5% down, 500–579 for 10% down.
- Stable employment and income history required.
- Must meet FHA appraisal standards, which can delay funding.
Additionally, FHA loans require mortgage insurance premiums (MIP), both upfront (1.75% of the loan amount) and annually (0.15%–0.75%, depending on loan term and LTV). These costs are baked into the overall cost of borrowing and can make FHA loans more expensive in the long run—even if the nominal interest rate appears lower.
fha vs conventional loan interest rates – Fha vs conventional loan interest rates menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Pros and Cons of FHA Interest Rates
One major advantage of FHA loans is consistency. Because they’re government-backed, rates tend to be more stable across lenders. You’re less likely to see wild swings in quotes. However, the lack of competition can also mean less incentive for lenders to offer discounts.
- Pros: Easier qualification, consistent pricing, lower down payment.
- Cons: Mandatory mortgage insurance for life (if loan originated after June 2013), limited loan limits, property must meet HUD standards.
For borrowers in rural or lower-value markets, FHA loans can be a lifeline. But for those in high-cost areas, the FHA loan limit ($498,257 in most areas in 2024) may not be enough to cover home prices, forcing a shift to jumbo conventional loans.
“FHA loans are a great tool for entry-level buyers, but they’re not always the cheapest option—even with lower rates advertised,” notes mortgage broker James Tran on National Mortgage News.
Decoding Conventional Loan Interest Rates
Conventional loans dominate the U.S. mortgage market, accounting for over 70% of originations in 2023, according to the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB). Their interest rates are influenced by a mix of market forces, borrower profile, and investor demand.
fha vs conventional loan interest rates – Fha vs conventional loan interest rates menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
What Drives Conventional Loan Pricing?
Unlike FHA loans, conventional loans are not government-insured. Instead, they’re backed by government-sponsored enterprises (GSEs) like Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, which set guidelines and purchase loans from lenders. This secondary market efficiency often leads to tighter spreads and lower rates—especially when the economy is stable.
- Borrower credit score: 740+ gets the best rates.
- Down payment: 20% avoids private mortgage insurance (PMI).
- Loan term: 15-year loans have lower rates than 30-year.
Investor appetite for mortgage-backed securities (MBS) also affects rates. When Treasury yields rise, mortgage rates typically follow. But conventional MBS are more liquid than FHA-insured securities, giving lenders more flexibility to offer competitive pricing.
When Conventional Loans Beat FHA on Rates
Borrowers with credit scores above 700 often find conventional loans cheaper than FHA—even with identical down payments. Why? Because lenders can price conventional loans more aggressively due to lower default risk and better resale value in the secondary market.
fha vs conventional loan interest rates – Fha vs conventional loan interest rates menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
For example, in Q2 2024, a borrower with a 720 credit score and 10% down payment might receive:
- FHA loan: 6.9% interest + 0.85% annual MIP = effective rate of ~7.75%
- Conventional loan: 6.6% interest + 0.45% PMI (can be removed later) = effective rate of ~7.05%
In this case, the conventional loan is clearly cheaper over time. Plus, PMI can be canceled once equity reaches 20%, while FHA MIP typically lasts 11 years or the life of the loan, depending on down payment and loan term.
“The myth that FHA loans always have lower rates is outdated. For well-qualified borrowers, conventional financing often wins on total cost,” says economist Dr. Maria Lopez of the Urban Institute.
FHA vs Conventional Loan Interest Rates: The Hidden Costs
When comparing FHA vs conventional loan interest rates, focusing only on the stated rate is a mistake. Hidden fees and insurance requirements can dramatically alter the true cost of borrowing.
fha vs conventional loan interest rates – Fha vs conventional loan interest rates menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Mortgage Insurance: The Game Changer
This is where the real difference lies. FHA loans require two types of mortgage insurance:
- Upfront MIP: 1.75% of the loan amount, often financed into the loan.
- Annual MIP: Ranges from 0.15% to 0.75%, paid monthly.
For a $300,000 loan, that’s $5,250 in upfront MIP and $1,800–$2,250 annually. And if you put less than 10% down, you’ll pay MIP for the life of the loan.
Conventional loans, on the other hand, require PMI only if you put down less than 20%. PMI rates range from 0.22% to 1.00%, but crucially, it can be removed once your loan-to-value ratio hits 80%. This flexibility makes conventional loans more cost-effective over time.
fha vs conventional loan interest rates – Fha vs conventional loan interest rates menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Other Fees to Watch For
Both loan types come with closing costs, but FHA loans may have additional fees due to stricter appraisal rules. FHA appraisals include health and safety inspections, which can lead to repair requirements that delay closing or increase costs.
- FHA: Appraisal fees, upfront MIP, funding fees.
- Conventional: Origination fees, credit report, title insurance, PMI (if applicable).
On average, closing costs for both loan types range from 2% to 5% of the loan amount. However, FHA borrowers may face higher out-of-pocket costs if the home fails the FHA inspection and the seller refuses to make repairs.
“The appraisal process for FHA loans can be a hidden cost driver. What seems like a lower rate can turn into a more expensive transaction,” warns real estate attorney Karen Wu.
Which Loan Type Offers Better Long-Term Value?
When evaluating FHA vs conventional loan interest rates, it’s essential to look beyond the first few years. Long-term value depends on your financial goals, how long you plan to stay in the home, and your ability to build equity.
fha vs conventional loan interest rates – Fha vs conventional loan interest rates menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Total Cost of Ownership Over 30 Years
Let’s compare a $350,000 home with 10% down ($35,000) and a 30-year fixed mortgage:
- FHA Loan: 6.9% interest, $315,000 loan amount, $5,512.50 upfront MIP, $2,100 annual MIP.
- Conventional Loan: 6.6% interest, $315,000 loan amount, $1,417.50–$3,150 annual PMI (estimated), removable after 8–10 years.
Over 30 years, the FHA loan could cost $60,000–$80,000 more due to lifelong mortgage insurance. Even with a slightly lower interest rate, the conventional loan wins if the borrower stays past the PMI removal point.
Refinancing Flexibility
Conventional loans offer more refinancing options. You can refinance to eliminate PMI once you reach 20% equity. FHA loans, however, require a full refinance (FHA-to-FHA or FHA-to-conventional) to remove MIP, which means new closing costs and credit checks.
fha vs conventional loan interest rates – Fha vs conventional loan interest rates menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Conventional: Streamline refinance options available.
- FHA: Limited streamline options; often requires full underwriting.
Borrowers who improve their credit or home value over time may find it easier and cheaper to refinance a conventional loan than an FHA one.
How Credit Score Impacts FHA vs Conventional Loan Interest Rates
Your credit score is one of the most powerful factors in determining your mortgage rate—regardless of loan type. But the impact varies between FHA and conventional loans.
FHA Loans: More Forgiving, But Not Cheaper
FHA loans accept lower credit scores, but that doesn’t mean you’ll get a better rate. In fact, lenders often charge higher interest to borrowers with scores below 680 to offset risk. While FHA allows a 580 minimum, many lenders impose overlays requiring 620+ for approval.
fha vs conventional loan interest rates – Fha vs conventional loan interest rates menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- 620–639: Likely to see rates 0.5%–1.0% above prime.
- 640–679: Moderate risk pricing.
- 680+: Competitive rates, but still may trail conventional offers.
Because FHA loans are seen as riskier by investors, the pricing structure doesn’t reward credit improvement as aggressively as conventional loans.
Conventional Loans: Credit Score Matters More
Conventional loans are highly sensitive to credit tiers. A jump from 680 to 740 can save you 0.75% or more on your interest rate. Lenders use “price adjustments” based on credit score bands, and higher scores unlock significant savings.
- 740–850: Best available rates.
- 700–739: Slight increase (0.25%–0.50%).
- 660–699: Moderate increase (0.50%–1.00%).
- Below 660: May face higher rates or denial.
If you’re willing to wait and improve your credit, a conventional loan can offer far greater long-term savings than an FHA loan—even with a slightly higher down payment.
fha vs conventional loan interest rates – Fha vs conventional loan interest rates menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
“A 70-point credit score improvement can save you over $100 per month on a $300,000 loan. That’s $36,000 over 30 years,” says financial educator Tyrone Ross.
How to Choose: FHA vs Conventional Loan Interest Rates in Real Life
The decision between FHA and conventional loans isn’t just about interest rates—it’s about your entire financial picture. Here’s how to make the right choice.
Choose FHA If…
You’re a first-time homebuyer with limited savings and a credit score below 680. FHA loans make homeownership possible when conventional financing isn’t an option. The lower down payment and flexible qualification rules can be a game-changer.
- You have a credit score between 580–679.
- You can’t afford a 20% down payment.
- You’re buying a fixer-upper that meets FHA standards.
Just be aware of the lifelong mortgage insurance and potential resale challenges if the home needs repairs.
fha vs conventional loan interest rates – Fha vs conventional loan interest rates menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Choose Conventional If…
You have a credit score above 700, stable income, and can put down at least 10%. Even with PMI, conventional loans often offer better long-term value, lower rates, and more flexibility.
- You want to avoid lifelong mortgage insurance.
- You plan to refinance or build equity quickly.
- You’re buying in a high-cost area exceeding FHA loan limits.
Conventional loans also offer more loan term options (10, 15, 20, 30 years) and interest-only products for qualified borrowers.
FHA vs Conventional Loan Interest Rates: Expert Tips to Save Money
Whether you go FHA or conventional, there are smart strategies to reduce your interest rate and overall cost.
fha vs conventional loan interest rates – Fha vs conventional loan interest rates menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Shop Around and Compare Loan Estimates
Never accept the first quote. Get at least three Loan Estimates from different lenders. Compare not just interest rates, but also points, fees, and total closing costs. The CFPB’s Loan Estimate tool helps you compare offers side-by-side.
- Ask for a breakdown of all fees.
- Compare APR (Annual Percentage Rate), which includes fees and interest.
- Negotiate lender credits to reduce upfront costs.
Consider Paying Points
Paying discount points (1% of the loan amount per point) can lower your interest rate by 0.25% or more. This makes sense if you plan to stay in the home long-term.
- 1 point on a $300,000 loan = $3,000.
- Saving 0.25% on a 6.5% rate = ~$45/month.
- Break-even point: ~5.5 years.
If you plan to stay 7+ years, paying points can save thousands.
fha vs conventional loan interest rates – Fha vs conventional loan interest rates menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Improve Your Credit Before Applying
Even a small credit score boost can lead to a better rate. Pay down credit card balances, correct errors on your report, and avoid new credit inquiries before applying.
- Reduce credit utilization to under 30%.
- Check reports at AnnualCreditReport.com.
- Dispute inaccuracies with credit bureaus.
A 50-point increase can move you into a better pricing tier and save you tens of thousands over the loan’s life.
What is the main difference between FHA and conventional loan interest rates?
fha vs conventional loan interest rates – Fha vs conventional loan interest rates menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
The main difference lies in how rates are influenced by borrower risk and mortgage insurance. FHA loans often have slightly higher interest rates and require lifelong mortgage insurance for low down payments, while conventional loans can offer lower rates for borrowers with strong credit and allow PMI removal after reaching 20% equity.
Is it easier to get approved for an FHA loan than a conventional loan?
Yes, FHA loans have more lenient credit and down payment requirements, making them easier to qualify for, especially for first-time buyers or those with lower credit scores. However, lenders may impose stricter overlays, so approval isn’t guaranteed.
fha vs conventional loan interest rates – Fha vs conventional loan interest rates menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Can I refinance an FHA loan to a conventional loan?
Yes, you can refinance an FHA loan to a conventional loan through a rate-and-term refinance. This is a common strategy to eliminate lifelong mortgage insurance once you’ve built 20% equity in your home.
Do conventional loans always have lower interest rates than FHA loans?
Not always. While conventional loans often have lower rates for borrowers with good credit, FHA rates can sometimes be competitive—especially for those with lower credit scores. Always compare total costs, including insurance and fees.
How much can I save by choosing a conventional loan over an FHA loan?
Savings depend on your credit score, down payment, and loan amount. For a $300,000 loan, choosing a conventional loan with a lower rate and removable PMI could save $50,000–$80,000 over 30 years compared to an FHA loan with lifelong MIP.
In the battle of FHA vs conventional loan interest rates, there’s no one-size-fits-all answer. Your credit score, down payment, financial goals, and housing market all play a role. FHA loans offer accessibility and lower entry barriers, but conventional loans often provide better long-term value, especially for borrowers with strong finances. The key is to look beyond the headline interest rate and evaluate the total cost of ownership. By shopping around, improving your credit, and understanding the full picture, you can make a confident, informed decision that saves you money for decades to come.
Further Reading: